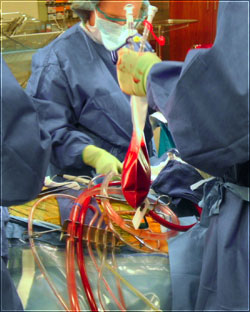
What is it & Methodology
What is the Hemobag®?
The Hemobag® is an FDA-cleared autotransfusion product and method designed specifically for cardiac and other major surgeries involving large blood loss. It concentrates all functional components of anticoagulated whole blood — red blood cells, platelets, plasma proteins, and clotting factors — enabling fast return of a patient’s own blood. Unlike many salvage methods that only recover red cells, the Hemobag® preserves all constituents of whole blood while removing waste and excess fluids.
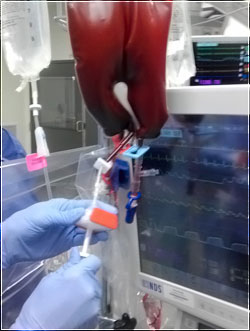
Why it matters
Better Coagulation & Hemostasis
Hemodilution and loss of clotting components during bypass surgery leads to a coagulopathy, bleeding, and transfusion exposure. The Hemobag® helps reverse those effects by returning all essential components quickly, only now concentrated.
Reduced Allogeneic Blood Use
By returning autologous whole blood, the Hemobag® helps reduce dependence on donor blood — lowering risks (transfusion reactions, infection), costs, and logistical demands.
Improved Patient Outcomes
Restoring plasma proteins, platelets, and clotting factors helps with overall stability after surgery, less postoperative bleeding, and more efficient recovery.
Comparative evidence and highlights
Understanding the data behind different blood management approaches is critical. The following studies compare outcomes across centrifugation, modified ultrafiltration, and Hemobag® systems so you can make informed clinical decisions.
Centrifugation vs. Multiple-Pass Hemoconcentration (MPH)
McNair et al. compared CF and MPH in a randomized controlled trial involving 61 adult patients. While hemoglobin levels post-surgery were similar between groups, the MPH group had significantly higher albumin, total protein, fibrinogen, and platelet counts. Importantly, MPH patients exhibited reduced allogeneic transfusion needs and improved fluid balance.
Online MUF vs. Off-Line MUF vs. Centrifugation
In another prospective study by McNair et al., 99 patients were divided into online MUF, off-line MUF, and CF groups. Off-line MUF (equivalent to HB) had the lowest transfusion rates (6.7%), followed by CF (14.7%) and online MUF (22.9%). Although online MUF showed the highest immediate hemoglobin recovery, fluid shifts appeared to inflate this benefit. Weight-adjusted analyses favored off-line MUF for actual hemoglobin retention and lowest fluid retention.
National Database Review – Hemobag Superiority
Baeza et al. analyzed 77,591 adult cardiac surgeries from the SCOPE registry. Five techniques were assessed: CF, UF, WB reinfusion, HB, and no processing. HB was associated with the lowest transfusion probability (0.79%) and the most favorable hematocrit recovery. Conversely, no post-CPB processing showed the highest transfusion rates. HB use reduced transfusion odds by half compared to CF, highlighting its clinical superiority.
Meta-Analysis of MUF Effectiveness
A comprehensive meta-analysis by Low et al. examined 13 randomized controlled trials involving 1,236 patients. MUF significantly increased post-CPB hematocrit, reduced chest tube drainage, decreased transfusion volumes (by ~0.73 units), and shortened ICU stay duration. Importantly, no increase in mortality or complications was observed. This solidified MUF’s status as both effective and safe for adult patients.
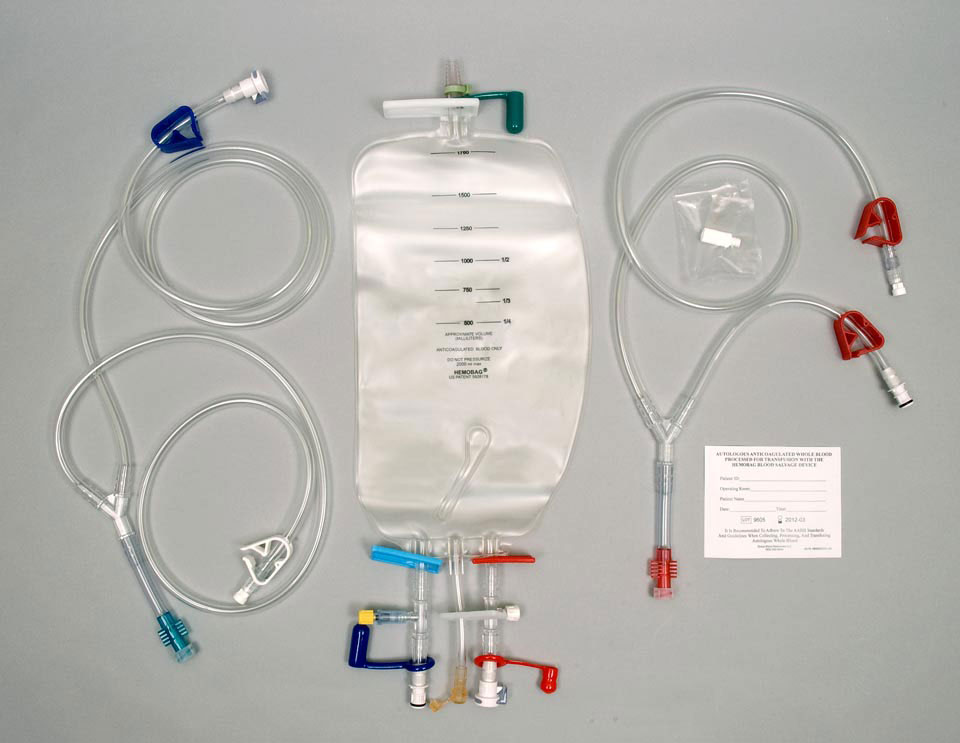
What’s included?
The standard order is made up of the following components:
Part No. GBR535 – 1 box contains 5 Hemobags and 5 TS3 Tubing Sets. The Hemobag and TS3 Tubing set must be used together and are not sold separately.
Learn More at our Legacy Site
For deeper info, case studies, clinical data, FAQs and protocol details, you can refer to:
Hemobag.com
Legacy site articles, protocols, and FAQs (linked above) contain full literature summaries, abstracts, and comparisons versus other blood salvage methods.